The method of thermography, based on the remote measurement of surface temperature distribution, was introduced into medicine in the mid-1950s and is now well known. The main characteristic of thermography in the study of living objects is that the method allows to objectively record changes in the intensity of heat emission and to perform thermal navigation of hyperthermal and hypothermic zones (projections of organs) on the human body.
The configuration VedaPulse + thermography software module allows doctors and wellness specialists to carry out a thermographic assessment of a person. Among the unconditional advantages of the method are non-invasiveness, absolute harmlessness and non-burden for the subject, the ability to quickly, in seconds, obtain a temperature image reflecting the current state of the whole body or a part of it.
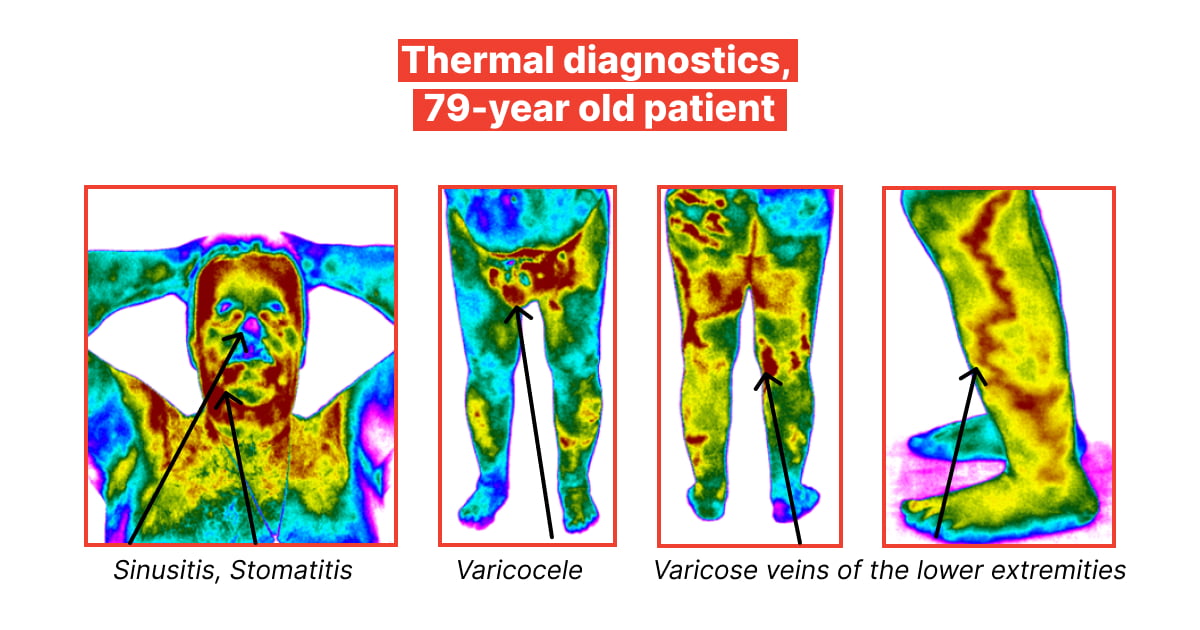
Let's look at some examples of how medicinal thermography can be used to safely diagnose and monitor the treatment of patients with inflammatory diseases of the nose and sinuses.
Case 1
The patient applied with the main diagnosis of varicocele (varicose veins of the spermatic cord that carry blood from the testicles) and with complaints of inflammation in the maxillary sinus. In the patient's medical history: cardiac dysrhythmia, problems with urination, violation of the processes of urination and water-salt metabolism. The images clearly show signs of the temperature increased field in the corresponding areas.

Case 2
The patient was diagnosed with chronic hypertrophic sinusitis of the left side. The diagnosis was confirmed in the ENT department of the health center and radiologically. In this case, the thermographic method allowed to detect an increase in temperature over the inflamed sinus on the right side, where the inflammatory and septic processes are more pronounced.
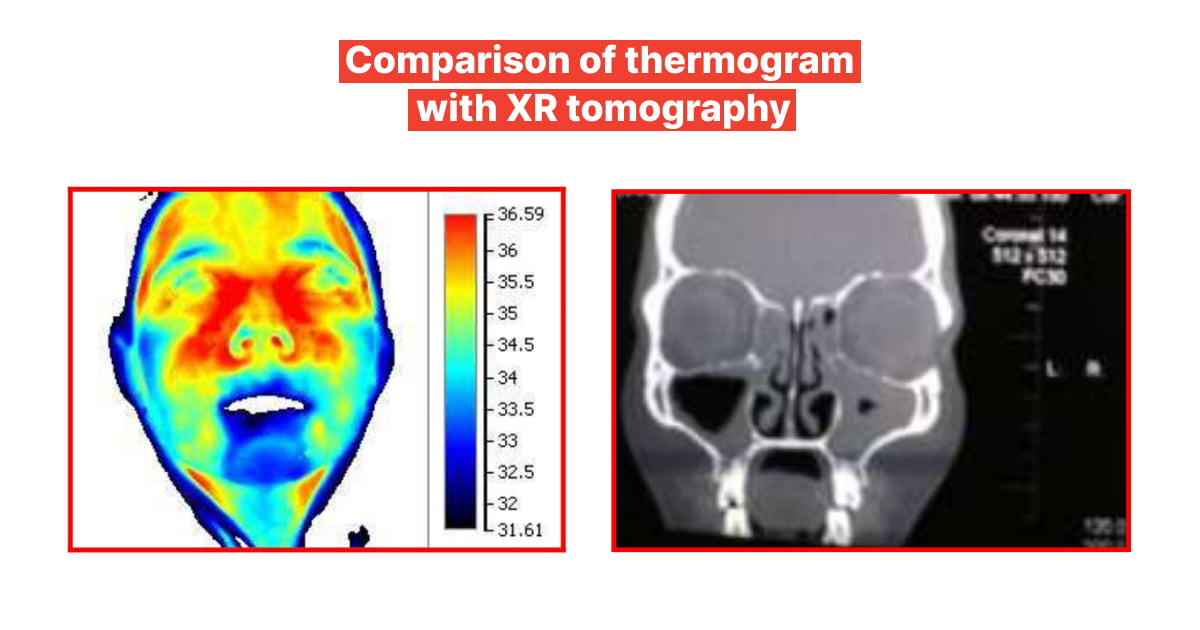
Thus, clinical examples clearly show how thermal imaging can be used to directly visualize the topography of pathology (which can be further detailed using other instrumental methods), to objectify clinical syndromes of disease, to determine the effectiveness of treatment and to make a short and long-term prognosis.